Publications and References

Back to top
Videos
RDD Response Guidance Videos
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory created a simulation that demonstrates the DHS RDD Response Guidance missions and tactics. Videos demonstrating these lifesaving tactics can be found on the Department of Homeland Security, Science and Technology YouTube channel.
Saving Lives After a Nuclear Detonation
This PrepTalk provides information on protective actions for a nuclear detonation and the many resources and tools for emergency managers that support planning, public education, and crisis communications. Emergency managers should use the video and these discussion materials to develop strategies for response plans, immediate public alerts and warnings, and emergency responder safety.
How to Protect Yourself After a Nuclear Explosion
FEMA’s animated video demonstrates how protecting yourself from high levels of radiation after a nuclear explosion COULD save your life. Learn the steps to reduce your risks from radiation. Accessible in American Sign Language and open captioning.
CDC’s Where to Go in a Radiation Emergency
To protect yourself in a radiation emergency, you should Go Inside, Stay Inside, and Stay Tuned. This animated infographic shows you where to shelter in a radiation emergency, and how to take these important protective steps.
Reducing Consequences of Nuclear Detonation
This presentation was delivered in January of 2010 at the Radiation Preparedness and Clinical Applications Seminar sponsored by Los Angeles County Radiation Management.
TED-Ed Animation: Can you Survive Nuclear Fallout?
Nuclear weapons are some of the most powerful tools of destruction on Earth, and the full scope of a nuclear detonation is almost unimaginable. However, there is a scientifically supported plan of action that could save thousands of lives. What is this plan, and what exactly would it protect us from? Brooke Buddemeier and Jessica S. Wieder explore the possibility of surviving nuclear detonation.
National & Federal Guidance

Planning Guidance for Response to a Nuclear Detonation, 3rd Ed. (May 2022)
Development coordinated by FEMA’s CBRN Office. This interagency consensus document provides excellent background information on the effects of a nuclear detonation and key response recommendations. Its definition of zones (damage and fallout) are the standard for response planning and should be integrated into any planning process.

Nuclear Detonation Response Guidance: Planning for the First 72 Hours
This document delineates Missions and Tactics that should be executed by first responders, emergency managers, and other state, local, tribal, and territorial (SLTT) response organizations during the first minutes, hours, and days following a nuclear detonation. It includes guidance on how to protect the lives of first responders and the public, develop a common operating picture, establish a coordinated multi-jurisdictional response, and prepare for the integration of support arriving from other jurisdictions, states, and federal agencies across the country.

Radiological Dispersal Device (RDD) Response Guidance Planning for the First 100 Minutes Report and Video
This document and accompanying videos provides actionable guidance, sample text for an RDD response protocol, and annexed tools that can be used for local planning of an effective response to an RDD to protect first responders and the general public, and establish interagency coordination and integration of state and federal assets.

National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurement (NCRP) Report No. 165 - Responding to a Radiological or Nuclear Terrorism Incident: A Guide for Decision Makers
Released Feb 2011 and is a National Standard that supplies the science and builds on many of the concepts of the Planning Guidance. Although NCRP typically charges for it's reports, this report has been made available for free by the organization.

Nuclear/Radiological Incident Annex to the Response and Recovery Federal Interagency Operational Plans
The Nuclear/Radiological Incident Annex (NRIA) to the National Response Framework (NRF) describes the policies, situations, concepts of operations, and responsibilities of the Federal departments and agencies governing the immediate response and short-term recovery activities for incidents involving release of radioactive materials to address the consequences of the event.

The Protective Action Guide (PAG) Manual
The PAG Manual contains radiation dose guidelines that would trigger public safety measures, such as evacuation or staying indoors, to minimize or prevent radiation exposure during an emergency. EPA developed Protective Action Guides to help responders plan for radiation emergencies.
References for the Response Community

The Health and Safety Planning Guide
Response in the aftermath of a nuclear detonation will be extremely challenging. The Health and Safety Planning Guide for Planners, Safety Officers, and Supervisors for Protecting Responders Following a Nuclear Detonation (visit website) provides planners and responders a better understanding for addressing the unique risks encountered in the post-IND environment.

IND Quick Reference Guide for Planners, Safety Officers, and Supervisors for Protecting Responders
The accompanying quick reference guide, “IND Quick Reference Guide for Planners, Safety Officers, and Supervisors for Protecting Responders” (visit website) provides response planners, safety officers, and supervisors with specific information and recommendations to protect responders from the effects and impacts of an extreme event: a 10 kiloton (KT) improvised nuclear device (IND) within the first 72 hours of a detonation.

Guidance for Emergency Response Dosimetry
NCRP Report No. 179, Guidance for Emergency Response Dosimetry, by the National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements, 2017, 180 pages hardcopy/electronic), $75.00/$60.00. This Report bridges the dosimetry gaps between trained and equipped radiation workers and all other categories of responders who are considered emergency workers during a response to a radiological or nuclear incident. It provides guidance on the control of radiation dose. This Report discusses a scalable approach for optimizing and repurposing existing equipment and provides tools that help emergency managers and planners identify the best available equipment for a specific mission.

Nuclear Detonation Fallout: Key Considerations for Internal Exposure and Population Monitoring
Nuclear Detonation Fallout: Key Considerations for Internal Exposure and Population Monitoring (Buddemeier, LLNL-TR-754319) reviews fallout properties and summarizes information related to external and internal fallout exposure hazards. It also reviews current information on population monitoring and decontamination recommendations.
References for the Medical Community

A Decision Makers Guide: Medical Planning and Response for a Nuclear Detonation
This document assists preparedness efforts and decision making by providing readily accessible information that quickly describes critical scientific and medical aspects of a nuclear incident as well as the response organization and resources anticipated to be required or available during a response. It is intended to offer a checklist of decision-provoking questions and reference guide for essential information to assist with the development of appropriate actions in response to a nuclear detonation. The subject matter includes basic principles about radiation, measurement, health effects, protective actions, critical public messaging, response strategies, medical management and countermeasures, and preparedness for a nuclear detonation.

Radiological Emergency Medical Management (REMM)
The REMM website provides:
- Guidance for health care providers, primarily physicians, about clinical diagnosis and treatment of radiation injury during radiological and nuclear emergencies.
- Just-in-time, evidence-based, usable information with enough background and context to make complex issues understandable to those without formal radiation medicine expertise.
- Web-based information that is also downloadable in advance, so that it would be available during an emergency if the internet is not accessible.
References for Communication

CBRN Responder Public Information Resource Library
CBRN Responder reference library contains a variety of communication tools, references, templates, and videos from a variety of agencies. CBRNResponder is sponsored by FEMA and other federal agencies to be your one-stop shop for RadResponder, ChemResponder, BioResponder, and IMAAC products. CBRNResponder is the headquarters for incident data sharing, multi-hazard event management, and integrates with federal assets.

EPA PAG Public Communication Resources website
This website contains key communication references from a variety of communication tools, references, and templates from a variety of agencies. During a radiological or nuclear emergency, clear and consistent messaging is important. The federal government has created several pre-scripted, focus-group tested messages to help emergency response departments, agencies, and individuals communicate radiation information and public safety measures with affected populations.
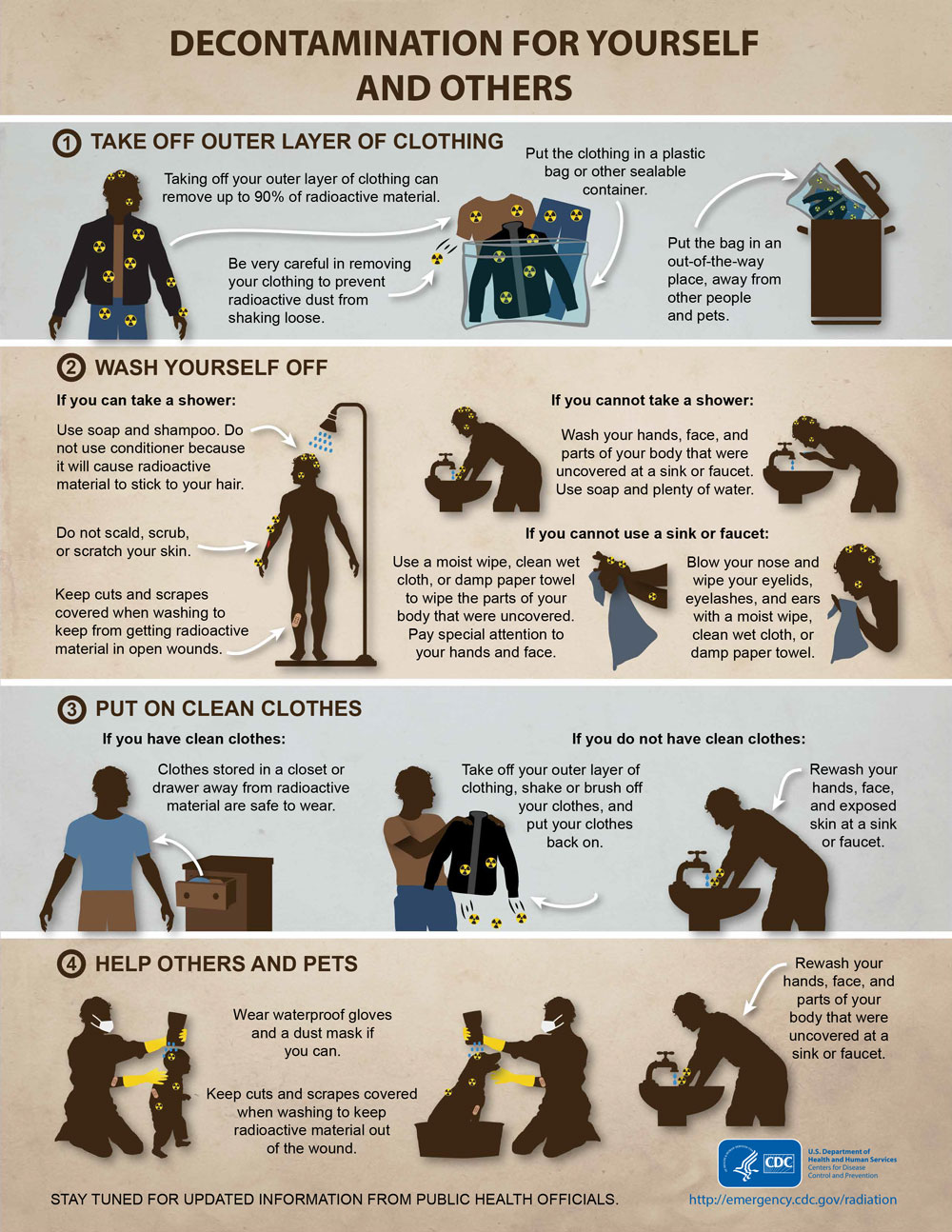
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC’s) Radiation Emergency Infographics website
The CDC's website contains 16 infographics ranging across types of radiation emergencies to safety messages to medical countermeasures. The infographics are translated into many different languages.

The Federal Emergency Management Agency’s (FEMA’s) Improvised Nuclear Device Response and Recovery: Communicating in the Immediate Aftermath
This document provides pre-approved questions and answers to anticipated questions from the public and the media for after the explosion of an improvised nuclear device.

Ready.gov Be Informed: Nuclear Explosion
This web page has instructions on how to stay safe during and after a nuclear explosion. It links to FEMA’s Be Prepared for a Nuclear Explosion information sheet, which is available in PDF form. It also includes a preparedness video with hardcoded subtitles and American Sign Language (ASL) translation.

Department of Homeland Security’s (DHS) Annex N (Radiological) to Emergency Support Function #15 External Affairs
This document details radiological incident communications strategies and actions and provides a resource list for other communications tools available from the federal government. It includes pre-approved social media messages that are compatible with Twitter and the Integrated Public Alert and Warning System.

Communicating Radiation Risks: Crisis Communications for Emergency Responders
Guidance on communications techniques based on proven risk and crisis communication strategies as well as radiological scenarios and messages for use in radiological emergencies.

Protective Action Questions & Answers for Radiological and Nuclear Emergencies
This document includes pre-scripted radiation emergency public safety messages intended to help emergency planners prepare public communications prior to and during a radiological emergency (visit website).

Protective Action Area Map Templates (.docx)
Templates (10 pp, 16 MB, September 2017, EPA-420/K-17/003) for state, local, and tribal governments that need to provide evacuation, go inside, food, and/or drinking water guidance quickly to a population in a specific geographical area.
Additional Resources

Tools Sponsored by the Office of Emerging Threats
FEMA has developed and sponsored a standardized suite of response capabilities for federal, state, local, tribal and territorial emergency responders and planners to rapidly and effectively minimize loss of life, protect the environment and maintain the economy.

Key Response Planning Factors for the Aftermath of Nuclear Terrorism
Developed by LLNL in support of the Department of Homeland Security Office of Health Affairs. It was released in August 2009 and identified key response issues associated with a nuclear detonation.

The Key Planning Factors for Recovery from a Radiological Terrorism Incident
A document developed by LLNL under contract to DHS S&T as part of the Wide Area Resiliency and Recovery Program (WARRP). It is designed to identify key planning factors that could substantially aid the recovery process by decreasing the recovery timeline and costs, improving public health and safety, and addressing major resource limitations and critical decisions.

National Academies Bridge Journal on Nuclear Dangers
An article written by LLNL, highlights recent research over the last few years that has helped greatly improve our understanding of appropriate actions for the public and responder community to take after a nuclear detonation.






